Web Interface¶
Overview¶
EC3 as a Service (EC3aaS), is a web service offered to the community to facilitate the usage of EC3 to non-experienced users. Anyone can access the website and try the tool by using the user-friendly wizard to easily configure and deploy Virtual Elastic Clusters on multiple Clouds. The service does not require any account to use it. The user only needs to choose the Cloud provider and provide its credentials to allow EC3 to provision VMs from the underlying Clouds on behalf of the user.
Configuration and Deployment of a Cluster¶
In order to configure and deploy a Virtual Elastic Cluster using EC3aaS, a user accesses the homepage and selects “Deploy your cluster!” (Fig. 1). With this action, the web page will show different Cloud providers supported by the web interface version of EC3. Notice that not all the Cloud providers supported by EC3 appear in the website, only the most important providers in the field of research are currently supported by the web version. Users that want to use another supported Cloud provider, such as Microsoft Azure or Google Cloud Engine, are encouraged to use the CLI interface.

Fig 1. EC3aaS homepage.
The first step, then, is to choose the Cloud provider where the cluster will be deployed (Fig. 2).

Fig 2. Deploy and Manage section of the website.
When the user chooses the deployment of a new infrastructure, a wizard pops up (Fig. 3). This wizard will guide the user during the configuration process of the cluster, allowing to configure details like the operating system, the characteristics of the nodes, the maximum number of nodes of the cluster or the pre-installed software packages.
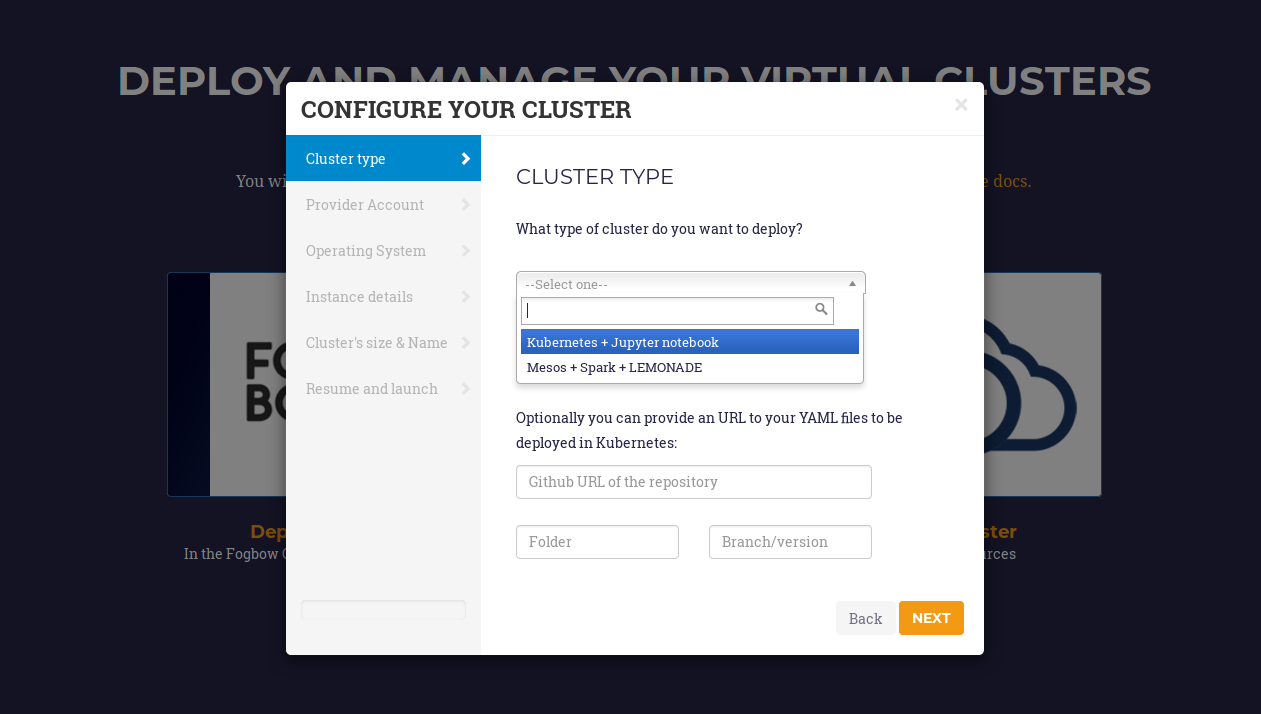
Fig 3. Wizard to configure and deploy a virtual cluster in Fogbow.
Specifically, the wizard steps are:
- Cluster Type: the user first selects the type of cluster he/she wants to deploy. Currently, there are two different options: Kubernetes + Jupyter Notebook or Mesos + Spark + Lemonade. Moreover, on the bottom of this step, there is an option to indicate the github URL where deployments of the user apps are. This only works together with the Kubernetes option.
- Provider account: Valid user credentials are required to access to the resources of Fogbow. The wizard then is able to contact with Fogbow to generate the token by using the user credentials.
- Operating System: the user can choose the OS of the cluster, by using a select box where the available images of Fogbow for its credentials are listed (Fig. 4) . It takes some seconds to appear, because a call to the Fogbow’s API is performed.
- Instance details: the user must indicate the instance details, like the number of CPUs or the RAM memory, for the front-end and also the working nodes of the cluster.
- Cluster’s size & Name: the user can introduce the maximum number of nodes of the cluster, without including the front-end node. This value indicates the maximum number of working nodes that the cluster can scale. Remember that, initially the cluster only is created with the front-end, and the nodes are powered on on-demand. Also, a unique name is required by the user for the cluster.
- Resume and Launch: a summary of the chosen configuration of the cluster is showed to the user at the last step of the wizard, and the deployment process can start by clicking the Submit button.
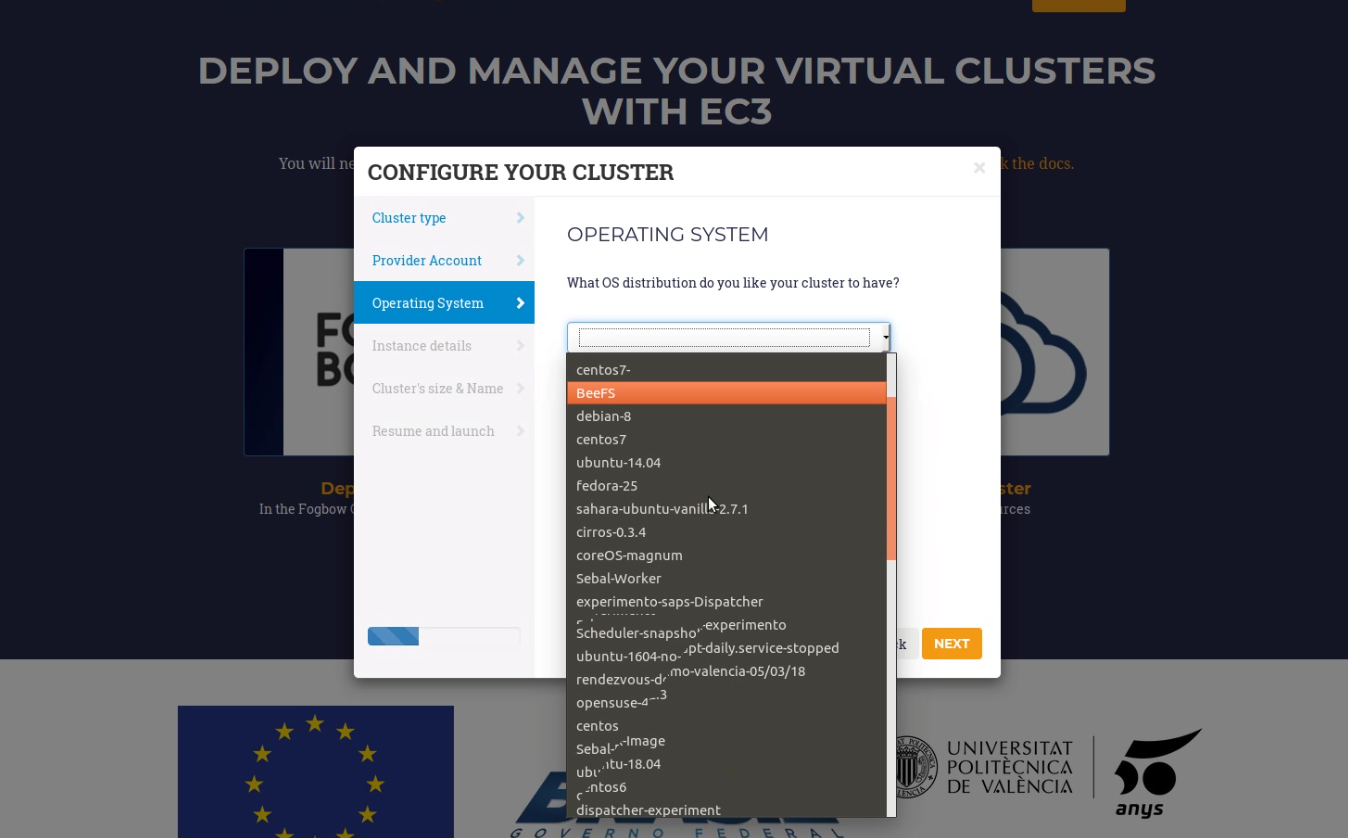
Fig 4. List of available OS in Fogbow.
Finally, when all the steps of the wizard are filled correctly, the submit button starts the deployment process of the cluster. Only the front-end will be deployed, because the working nodes will be automatically provisioned by EC3 when the workload of the cluster requires them. When the virtual machine of the front-end is running, EC3aaS provides the user with the necessary data to connect to the cluster (Fig. 4) which is composed by the username and password to connect to the cluster, the front-end IP and the name of the cluster. The user must keep this data during the lifetime of the cluster, since it is used also to terminate it. The cluster may not be configured when the IP of the front-end is returned by the web page, because the process of configuring the cluster is a batch process that takes several minutes, depending on the chosen configuration. However, the user is allowed to log in the front-end machine of the cluster since the moment it is deployed. To know if the cluster is configured, the command is_cluster_ready can be used. It will check if the configuration process of cluster has finished:
ubuntu@kubeserverpublic:~$ is_cluster_ready
Cluster configured!
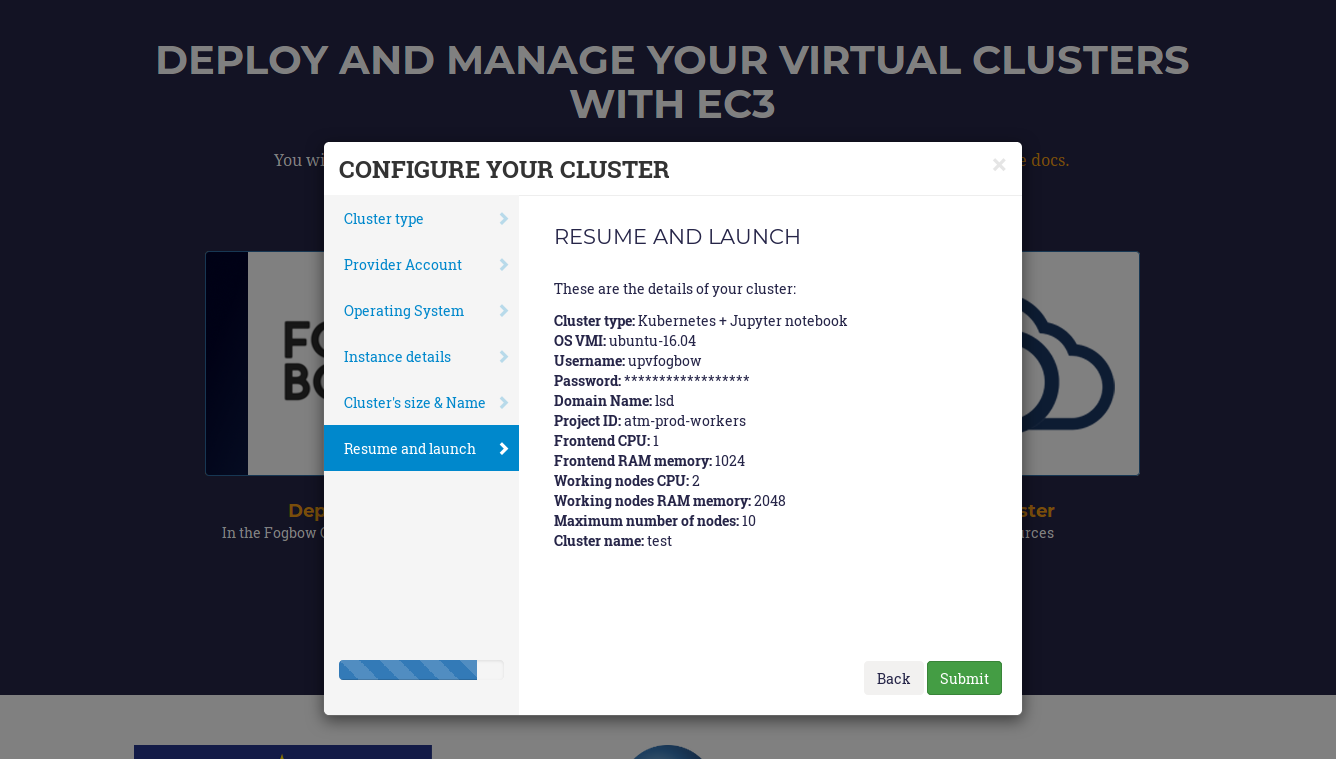
Fig 5. Information received by the user when a deployment succeeds.
Notice that EC3aaS does not offer all the capabilities of EC3, like hybrid clusters or heterogeneous nodes. Those capabilities are considered advanced aspects of the tool and are only available via the EC3 Command-line Interface.
Termination of a Cluster¶
To delete a cluster the user only needs to access the EC3aaS webpage, and click on the “Delete your cluster” button. He/she must indicate in the wizard (Fig. 5) the cluster name provided in the deployment phase and the Fogbow credentials again, to generate the token in order to destroy the resources. The cluster name is a string composed by the name given to the cluster in the deployment process followed by a random string of five characters (including numbers and letters). This cluster name is unique and allows EC3 to identify the cluster of the user without using an user account.
When the process finishes successfully, the front-end of the cluster and all the working nodes had been destroyed and a message is shown to the user informing the success of the operation. If an error occurs during the deleting process (for example, the indicated cluster name does not exist), an error message is returned to the user.
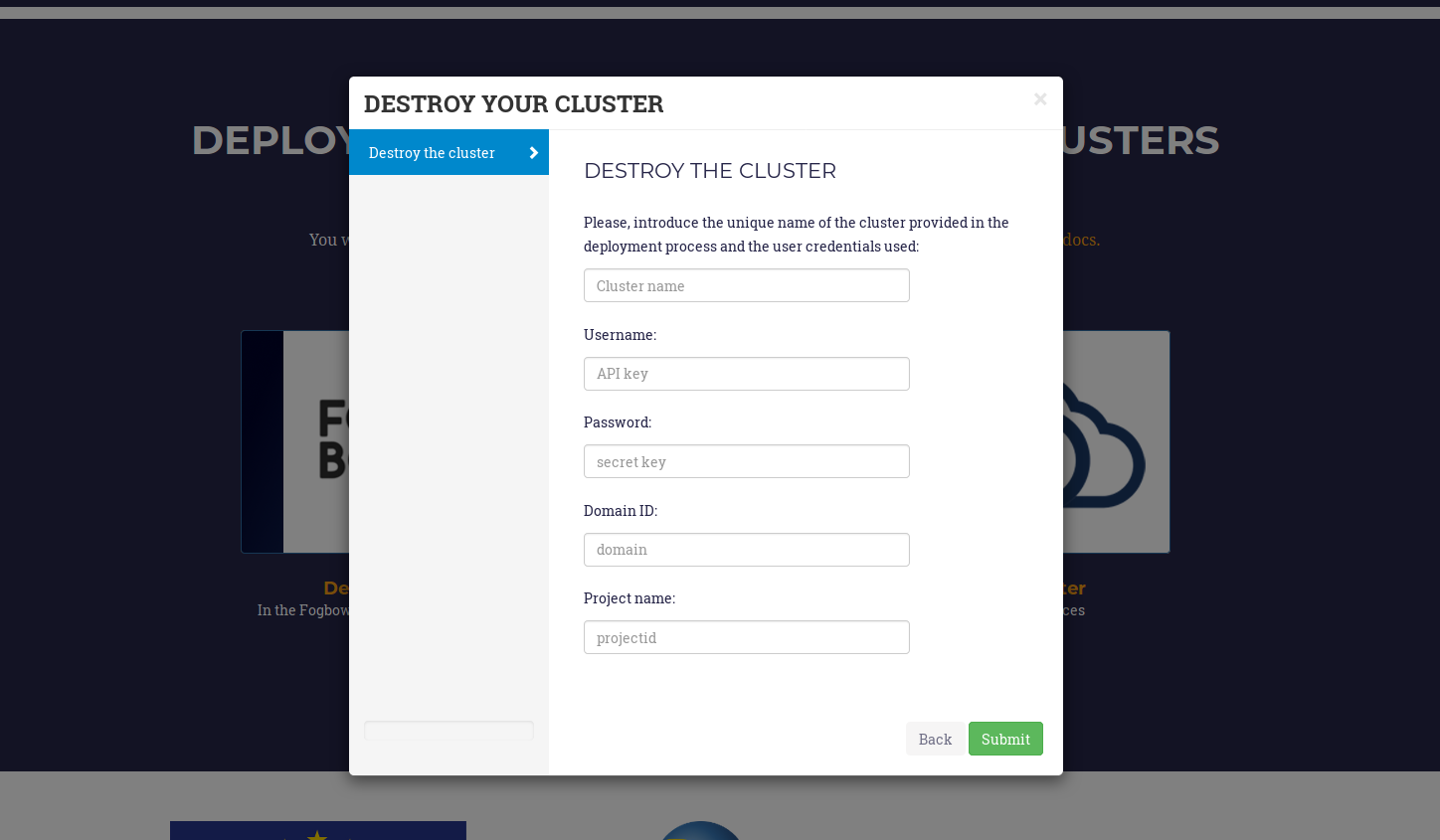
Fig 6. Wizard to delete a cluster.
Additional information¶
You can find interesting reading also: